在这篇文章里,我想和你分享22个python代码片段,可以帮你解决一些日常问题。
图片来自作者空格分隔多个输入这段代码可以让你一次进行多个用空格分隔的输入,每当你要解决编程竞赛的问题时,这段代码就可以派上用场## Taking Two Integers as input a,b = map(int,input().split()) print("a:",a) print("b:",b) ## Taking a List as input arr = list(map(int,input().split())) print("Input List:",arr)。
2. 同时访问Index索引和值enumerate()这个内置函数可以让你在or循环中同时找到索引和值arr = [2,4,6,3,8,10] for index,value in enumerate(arr): print(f"At Index {index} The Value Is -> {value}") Output At Index 0 The Value Is -> 2 At Index 1 The Value Is -> 4 At Index 2 The Value Is -> 6 At Index 3 The Value Is -> 3 At Index 4 The Value Is -> 8 At Index 5 The Value Is -> 10 。
3. 检查内存使用情况这段代码可以用于检查对象的内存使用情况。

4. 输出某个变量的唯一IDid()这个函数能让你找到变量的唯一id,你只需要在这个方法中传递变量名。

5. 检查Anagram一个Anagram的意思是,通过重新排列一个单词的字母,在恰好使用一次每个原始字母的情况下,组成另一个新词def check_anagram(first_word, second_word): return sorted(first_word) == sorted(second_word) print(check_anagram("silent", "listen")) # True print(check_anagram("ginger", "danger")) # False。
6. 合并两个字典当你在处理数据库和JSON文件,需要将来自不同文件或表的多个数据合并到同一个文件中时,用这个代码会很方便合并两个字典会有一些风险,比如要是出现了重复的key怎么办?还好,我们对这种情况也是有解决方案的。
basic_information = {"name":[karl,Lary],"mobile":["0134567894","0123456789"]} academic_information = {"grade":["A","B"]} details = dict() ## Combines Dict ## Dictionary Comprehension Method details = {key: value for data in (basic_information, academic_information) for key,value in data.items()} print(details) ## Dictionary unpacking details = {**basic_information ,**academic_information} print(details) ## Copy and Update Method details = basic_information.copy() details.update(academic_information) print(details)
7. 检查一个文件是否存在我们要确保代码中使用的文件还存在Python使管理文件变得很容易,因为Python有读写文件的内置语法# Brute force Method import os.path from os import path def check_for_file(): print("File exists: ",path.exists("data.txt")) if __name__=="__main__": check_for_file() File exists: False 。
8. 在给定范围内,算所有数的平方在这段代码中,我们利用内置函数itertools找到给定范围内每个整数的平方# METHOD 1 from itertools import repeat n = 5 squares = list(map(pow, range(1, n+1), repeat(2))) print(squares) # METHOD 2 n = 6 squares = [i**2 for i in range(1,n+1)] print(squares) """Output [1, 4, 9, 16, 25] """。
9. 将两个list转换为dictionary以下这个方法可以将两个列表转换为字典list1 = [karl,lary,keera] list2 = [28934,28935,28936] # Method 1: zip() dictt0 = dict(zip(list1,list2)) # Method 2: dictionary comprehension dictt1 = {key:value for key,value in zip(list1,list2)} # Method 3: Using a For Loop (Not Recommended) tuples = zip(list1, list2) dictt2 = {} for key, value in tuples: if key in dictt2: pass else: dictt2[key] = value print(dictt0, dictt1, dictt2, sep = "\n")。
10. 对字符串列表进行排序当你拿到一个学生姓名的列表,并想对所有姓名进行排序时,这段代码会非常有用list1 = ["Karl","Larry","Ana","Zack"] # Method 1: sort() list1.sort() # Method 2: sorted() sorted_list = sorted(list1) # Method 3: Brute Force Method size = len(list1) for i in range(size): for j in range(size): if list1[i] < list1[j]: temp = list1[i] list1[i] = list1[j] list1[j] = temp print(list1)。
11. 用if和Else来理解列表当你希望根据某些条件筛选数据结构时,这段代码非常有用。

12. 添加来自两个列表的元素假设你有两个列表,并想通过添加它们的元素将它们合并到一个列表中,这段代码在这种场景中会很有用maths = [59, 64, 75, 86] physics = [78, 98, 56, 56] # Brute Force Method list1 = [ maths[0]+physics[0], maths[1]+physics[1], maths[2]+physics[2], maths[3]+physics[3] ] # List Comprehension list1 = [x + y for x,y in zip(maths,physics)] # Using Maps import operator all_devices = list(map(operator.add, maths, physics)) # Using Numpy Library import numpy as np list1 = np.add(maths,physics) Output [137 162 131 142] 。
13. 对dictionary列表进行排序当你有一个字典列表时,你可能希望借助key的帮助将它们按顺序排列起来dict1 = [ {"Name":"Karl", "Age":25}, {"Name":"Lary", "Age":39}, {"Name":"Nina", "Age":35} ] ## Using sort() dict1.sort(key=lambda item: item.get("Age")) # List sorting using itemgetter from operator import itemgetter f = itemgetter(Name) dict1.sort(key=f) # Iterable sorted function dict1 = sorted(dict1, key=lambda item: item.get("Age")) Output [{Age: 25, Name: Karl}, {Age: 35, Name: Nina}, {Age: 39, Name: Lary}] 。
14. 计算Shell的时间有时,了解shell或一段代码的执行时间是很重要的,这样可以用最少的时间取得更好的算法# METHOD 1 import datetime start = datetime.datetime.now() """ CODE """ print(datetime.datetime.now()-start) # METHOD 2 import time start_time = time.time() main() print(f"Total Time To Execute The Code is {(time.time() - start_time)}" ) # METHOD 3 import timeit code = ## Code snippet whose execution time is to be measured [2,6,3,6,7,1,5,72,1].sort() print(timeit.timeit(stmy = code,number = 1000))。
15. 检查字符串中的子字符串我日常都会遇到的一件事,就是检查一个字符串是否包含某个子字符串与其他编程语言不同,python为此提供了一个很好的关键字addresses = [ "12/45 Elm street", 34/56 Clark street, 56,77 maple street, 17/45 Elm street ] street = Elm street for i in addresses: if street in i: print(i) output 12/45 Elm street 17/45 Elm street 。
16. 字符串格式代码最重要的部分是输入、逻辑和输出在编程过程中,这三个部分都需要某种特定格式,以得到更好地、更易于阅读的输出python提供了多种方法来改变字符串的格式name = "Abhay" age = 21 ## METHOD 1: Concatenation print("My name is "+name+", and I am "+str(age)+ " years old.") ## METHOD 2: F-strings (Python 3+) print(f"My name is {name}, and I am {age} years old") ## METHOD 3: Join print(.join(["My name is ", name, ", and I am ", str(age), " years old"])) ## METHOD 4: modulus operator print("My name is %s, and I am %d years old." % (name, age)) ## METHOD 5: format(Python 2 and 3) print("My name is {}, and I am {} years old".format(name, age))。
17. 错误处理与Java和c++一样,python也提供了try、except和finally 来处理异常错误的方法# Example 1 try: a = int(input("Enter a:")) b = int(input("Enter b:")) c = a/b print(c) except: print("Cant divide with zero") # Example 2 try: #this will throw an exception if the file doesnt exist. fileptr = open("file.txt","r") except IOError: print("File not found") else: print("The file opened successfully") fileptr.close() # Example 3 try: fptr = open("data.txt",r) try: fptr.write("Hello World!") finally: fptr.close() print("File Closed") except: print("Error")。
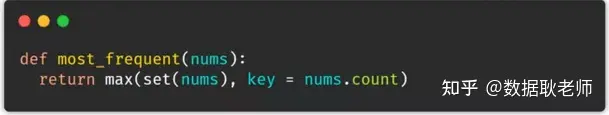
18. 列表中最常见的元素下面方法可以返回出列表中出现频率最高的元素。
19. 在没有if – else的情况下计算这段代码展示了在不使用任何if-else条件的情况下,如何简单地编写一个计算器import operator action = { "+" : operator.add, "-" : operator.sub, "/" : operator.truediv, "*" : operator.mul, "**" : pow } print(action[*](5, 5)) # 25。
20. Chained Function调用在python中,你可以在同一行代码调用多个函数def add(a,b): return a+b def sub(a,b): return a-b a,b = 9,6 print((sub if a > b else add)(a, b))。
21. 交换数值以下是在不需要另一个额外变量的情况下交换两个数值的快速方法a,b = 5,7 # Method 1 b,a = a,b # Method 2 def swap(a,b): return b,a swap(a,b)。
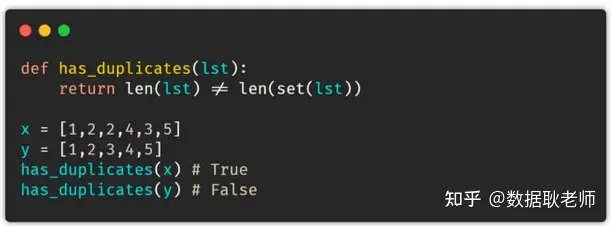
22. 查找重复项通过这段代码,你可以检查列表中是否有重复的值。
更多高质量科技类原创文章,请访问数据应用学院官网Blog:https://www.dataapplab.com/参加数据应用学院线上免费公开课:https://www.dataapplab.com/event/
查看数据应用学院往期课程视频:https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCa8NLpvi70mHVsW4J_x9OeQ

亲爱的读者们,感谢您花时间阅读本文。如果您对本文有任何疑问或建议,请随时联系我。我非常乐意与您交流。


发表评论:
◎欢迎参与讨论,请在这里发表您的看法、交流您的观点。